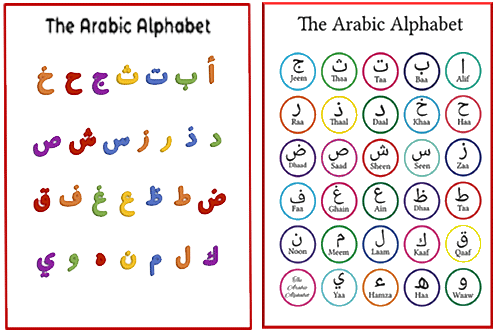
The Arabic alphabet consists of 28 letters, each with its own distinctive shape and sound. Some letters have similar shapes but are differentiated through dots or diacritical marks.
Table of Contents
ToggleEach letter represents a unique sound and plays a crucial role in forming words and conveying meaning in the Arabic language. However, there are two different views on the number of Arabic letters. Some say 29 letters, consider Alif and Hamza as two separate letters, and some say 28 letters and regard Hamza and Alif as one.
In addition to the 29 letters, three characters are written above and below other letters.
History
The Arabic alphabet has a rich history that dates back to the 4th century CE. Prior to the development of the Arabic script, the Arabic language was written using various scripts, including Nabatean and Syriac.
The Arabic alphabet was developed by the Nabateans, a group of traders who lived in the Arabian Peninsula. The Nabateans used an Aramaic script to write their language, but they modified it to suit their needs. They added new letters and changed the shapes of some of the existing letters.
Over time, the Arabic script evolved and became more standardized. In the 7th century CE, Islam emerged in Arabia, and the Arabic language became the language of the Quran. This led to a renewed interest in the Arabic script, and scholars worked to develop a more formalized system of writing.
During the Islamic Golden Age (8th-13th centuries CE), Arabic became a major language of science, philosophy, and literature. This led to further developments in the Arabic script, including the addition of diacritical marks to indicate vowel sounds.
Today, the Arabic alphabet is used to write not only Arabic but also other languages such as Persian, Urdu, and Kurdish. It is a beautiful and complex script that has played an important role in the history and culture of the Middle East.
How is the Arabic alphabet different from other writing systems?
The Arabic alphabet is a writing system used to write the Arabic language. It consists of 28 letters, written from right to left. Here are some ways in which the Arabic alphabet differs from other writing systems:
- Direction
The Arabic alphabet is written from right to left, whereas most writing systems are written from left to right. - Diacritical marks
The Arabic alphabet includes diacritical marks that indicate vowels and other features of pronunciation. Many other writing systems do not include such marks.
For example:
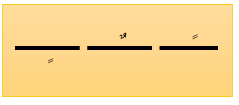
- Ligatures
Arabic letters can be joined together in various ways to form ligatures, which can change the shape of the letters. This is not common in most other writing systems. - Cursive script
Arabic is often written in a cursive script, meaning that the letters are connected to each other. This is also true of some other writing systems, such as Cyrillic.

- Calligraphy
Arabic calligraphy is a highly developed art form, with a long history and many different styles. This is not always true of many other writing systems.
The Arabic alphabet is a unique and distinctive writing system that has played an important role in the history and culture of the Middle East and beyond.
Some facts about Arabic alphabet
- Arabic letters have different forms
Arabic letters can have different shapes depending on their position in a word. There are four forms of each letter: initial, medial, final, and isolated. These forms change the way letters are written based on their position within a word.
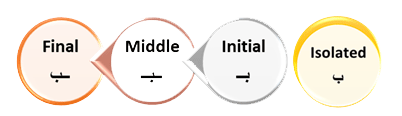
- Some letters have similar shapes
Arabic letters such as “ب” (ba), “ت” (ta), and “ث” (tha) have similar shapes but differ in the placement of dots or diacritical marks. These dots or marks are crucial in distinguishing between similar-looking letters. - The Nuances of Arabic Letters
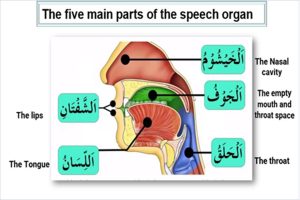
Each Quranic letter has its own unique manner of articulation, including points of pronunciation that distinguish it from other letters. For instance, the letters “ق” (qaf) and “ك” (kaf) have distinct throaty sounds that require precision in pronunciation. Learning these nuances contributes to the melodious and harmonious recitation of the Quran.
How should we learn Arabic alphabet?
- Start with the basics
Begin by learning the 28 letters of the Arabic alphabet. It’s important to learn the correct pronunciation and writing of each letter. - Practice writing
Practice writing each letter several times until you become comfortable with its shape and form. - Use flashcards
Use flashcards to memorize the letters and their corresponding sounds. - Listen to native speakers
Listen to native speakers of Arabic to get a better sense of how the letters are pronounced in context. - Use online resources
There are many online resources available to help you learn the Arabic alphabet, including interactive lessons, videos, and quizzes. - Join a class or find a tutor
Consider joining a class or finding a tutor who can provide personalized instruction and feedback as you learn the alphabet.
In conclusion, the Arabic alphabet is a fascinating writing system with a rich history and diverse uses. By learning more about its origins, unique features, and uses, we can gain a better understanding of the Arabic language and culture. Whether for practical or cultural reasons, acquiring proficiency in the Arabic alphabet can be a rewarding and valuable skill.
If you want to learn Arabic language from the basics (including the Arabic alphabet) to an advanced level, DarulQuran academy is the best option for of you. At DarulQuran Academy, we have successfully taught numerous individuals who were not initially familiar with Arabic, and they are now able to recite the Quran proficiently. These individuals started with our basic reading the Quran course and progressed to higher levels.
For more information, visit the DarulQuran Academ website:
https://darulquran.co.uk/courses/quran-reading/

















1 thought on “Arabic Alphabet (The Language of the Quran)”
Hi, it was great thanks alot.